2. Linux Shell
Linux Shell
The shell is an interface for you to interact with your operating system (OS). As you type commands into the shell, it's responsible for interpreting those commands.
Operations like copying files, piping, listing files are all within a shell's remit.
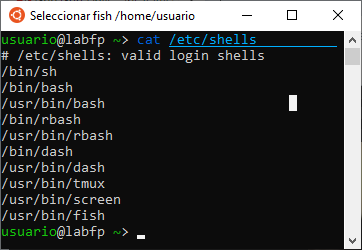
Several Linux shells are available. To find out all the shells that are available on your system, open the terminal and type:
cat /etc/shells
echo $0
If you want to use a different shell, you can simply type its name and you’ll be logged into the new shell. For example, if you install fish (sudo apt install fish) and want to use it, you can simply use:
to use fish
You can enter exit to exit from the new shell and return to the previous one.
2 Ways to Change a Users Default Shell in Linux:
usermod is a utility for modifying a user’s account details, stored in the /etc/passwd file and the -s or --shell option is used to change the user’s login shell.
In this example, we’ll first check user usuario’s account information to view his default login shell (cat /etc/passwd) and then change its login shell from /bin/bash to /bin/sh as follows.
In this example, we’ll first check user usuario’s account information to view his default login shell (cat /etc/passwd) and then change its login shell from /bin/bash to /bin/sh as follows.
NOTE: The sudo command will basically execute anything you want in the system as if the administrator's account ‘root’ was doing it.






Comentarios
Publicar un comentario